What Google MCM Means for Publishers
Google’s Multi-Client Management (MCM) is a recent development that has significant implications for publishers. It is a restructuring of the Google Ad Manager, a tool that enables publishers to sell their ad space. This new feature allows third-party companies, such as ad agencies or technology platforms, to manage ad inventories on behalf of multiple publishers. This means that publishers can entrust their ad operations to experts, freeing up their time and resources to focus on content creation and distribution. This is particularly beneficial for smaller publishers who may lack the expertise or resources to manage their own ad operations.
MCM also provides a consolidated view of all ad operations under one roof, making it easier to track performance and make strategic decisions. However, it also means that publishers would have less control over their ad operations, as they would be entrusting a significant aspect of their business to a third-party. It is therefore crucial for publishers to carefully consider the implications of MCM and decide whether it aligns with their business strategy.

What Publishers Need to Know
Publishers play a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge, literature, and culture in society. Their responsibilities extend beyond just printing and distributing books; they are also the gatekeepers who decide which works make it into the public domain. To do their job effectively, they need to be well-versed in several areas. Understanding the market is a primary concern; they need to know what readers want and how to provide it effectively. This includes being aware of current trends, popular genres, and potential niches that have not yet been explored. Additionally, they need to have a grasp of the financial aspects of publishing. This entails proper budgeting, pricing strategies, and understanding the economics of print vs. digital formats. Excellent communication skills are also paramount as they need to interact with authors, designers, editors, and booksellers.
They need to negotiate contracts, manage relationships, and resolve any potential issues that may arise. Furthermore, understanding the technicalities of book production, from the quality of paper to the typeface, is also crucial. Lastly, in this digital age, they must be familiar with the dynamics of online publishing and marketing, including social media promotion, eBook formats, and the ins and outs of audiobook production. Every publisher needs to continuously evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of the publishing industry to thrive and succeed. Being flexible and forward-thinking, while maintaining a deep respect for the written word and its power, is what makes a publisher truly successful.
What Actions Must Publishers Take?
Publishers play a pivotal role in the dissemination of information and literature, and they must undertake a series of actions to ensure a smooth and effective publishing process. Initially, they must rigorously vet and scrutinize manuscripts for quality, originality, relevance, and potential market appeal. This involves a detailed review of content, language, style, and structure, often facilitated by a team of editors and literary consultants.
Another crucial action is the negotiation and finalization of contracts with authors. This includes determining royalties, outlining the rights and responsibilities of both parties, and agreeing on timelines for publication. Publishers also need to arrange for professional editing, proofreading, and designing services to refine the manuscript and enhance its aesthetic appeal.
They are also responsible for devising and implementing comprehensive marketing and promotional strategies to generate anticipation and drive sales upon book release. This could encompass organizing book launches, securing reviews, facilitating author interviews, and leveraging social media platforms.

Furthermore, publishers must efficiently manage distribution channels to ensure the book reaches its intended audience. They need to forge partnerships with booksellers, libraries, online platforms, and other outlets, while also monitoring sales and inventory to avoid stock-out situations.
Finally, publishers need to stay abreast of the latest trends and developments in the publishing industry. They need to adapt and innovate in response to changes in reading habits, technological advancements, and market dynamics, while also maintaining a diverse and competitive portfolio of publications.
In conclusion, the actions that publishers must take are multifaceted and encompass several aspects, from manuscript selection and contract negotiation to book production, marketing, distribution, and industry trend analysis. These actions are vital to ensure the publication’s success and the satisfaction of authors and readers alike.
Understanding the Benefits of Google MCM for Publishers
Google Multi-Client Management (MCM) offers numerous advantages to publishers that enhance their visibility and control in the digital advertising realm. Firstly, it provides the opportunity for publishers to unify their programmatic deals under one umbrella, thereby simplifying the management of inventory and reducing inefficiencies. This streamlined approach makes it easier to oversee the entire advertising cycle, from setting up to monitoring and optimizing campaigns.
Moreover, Google MCM allows publishers to gain access to a wider network of advertisers. As a result, they can expand their reach, enhance their targeting, and consequently, bolster their revenue. It also offers transparency as publishers can view the performance of their inventory and make data-driven decisions to improve their advertising strategies.
In addition to this, Google MCM facilitates a more collaborative relationship between publishers and their partners. They can share their inventory with multiple partners simultaneously, which helps them to leverage the strengths of each partner and maximize their potential gains.
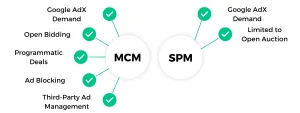
Furthermore, Google MCM helps publishers maintain control over their inventory. They can dictate the terms of their deals, set their pricing strategies, and choose who can access their inventory. This level of control ensures that publishers can protect their brand’s reputation and optimize their revenue stream.
Lastly, Google MCM is equipped with sophisticated technology that helps publishers navigate the complex world of digital advertising. For instance, it uses machine learning algorithms to predict the performance of different advertising strategies. This predictive capability can help publishers make informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve in the digital advertising landscape.
In summary, Google MCM equips publishers with the tools they need to effectively manage and optimize their digital advertising operations. By offering a unified platform, advanced technology, and enhanced control, it empowers publishers to maximize their revenue and stay competitive in the rapidly evolving digital advertising ecosystem.
Key Changes Publishers Should Be Aware Of with Google MCM
Google’s Multiple Customer Management system (MCM) has brought about significant changes that publishers need to be aware of to optimize their ad revenue and operations. These changes are primarily based on the way Google manages relationships with programmatic buyers. One of the most critical changes is that publishers, who were previously direct sellers, can now become inventory sources. This new status offers the potential for more visibility and control over transactions, as they can negotiate terms directly with advertisers.
Another significant change is the shift from the ‘seller of record’ model to the ‘agent of record’ model. Under the MCM, Google acts as the ‘agent of record’, handling all financial transactions and tax implications, thereby reducing the administrative burden on the publishers. This shift also ensures better transparency in the revenue chain, minimizing the opportunity for hidden fees.
Moreover, there has been a shift in the responsibility of policy enforcement and violations. Google now shares this responsibility with publishers, who are expected to tackle policy violations proactively. This new arrangement requires publishers to be more vigilant in monitoring their content and ad placements to prevent any policy breaches.
Finally, MCM brings changes to the way Google shares data. Publishers now have access to granular data about their inventory, such as impression-level data, which can be used to optimize their ad inventory and improve yield. This change requires publishers to invest in robust data analysis capabilities.
While these changes bring potential benefits, publishers need to be prepared to navigate the challenges that come with them. They need to understand the implications of these changes on their operations and revenue and take the necessary steps to adapt to this new environment.
